Overview
The Royce Deposition System at the University of Leeds is a multi-chamber, multi-technique facility for thin film growth. Comprised of four deposition chambers connected via ultra-high vacuum transfer chambers, the Royce Deposition System allows for different deposition techniques to be combined. The mission of this Technology Platform is to create multi-layered thin film exploiting interfaces between different types of materials. These interfaces open up new physics and the possibility of new functions for devices.
A key global challenge is to make computing and data storage more energy efficient; we need to reduce the power consumption and associated carbon emissions of our growing digital infrastructure. Current research using the Deposition System studies the physics of thin film-based materials and devices for low-energy computing. The Multi-chamber Deposition Technology Platform is integrated in the Atoms to Devices research theme within Royce.
KEY CAPABILITIES:
- Four connected deposition chambers
- Preparation chamber with heater and ion miller
- Sample sizes up to 2 inch wafers
- Substrate temperature from -100°C to 1200°C
- Load locks for fast sample turnaround
- UHV transfer chambers allow advanced heterostructures to be grown using multiple chambers and techniques
- Vacuum suitcase allows transfers to P-NAME (Manchester) for single-ion implantation
SCHEMATIC:
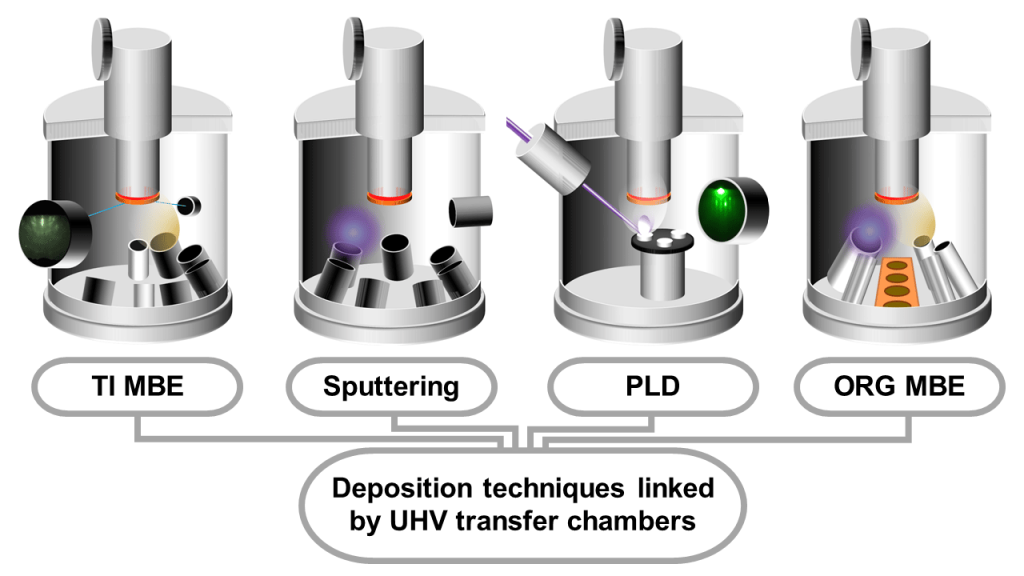

Topological Insulator Molecular Beam Epitaxy
This chamber is for the epitaxial growth of thin film topological insulators and topological superconductors. The system allows a wide range of alloys with precise stoichiometry aided by two high-temperature cracker cells.
- Four dual-filament effusion cells for deposition of materials such as bismuth selenide
- Low temperature effusion cell for deposition of low melting point metals such as indium
- Two valved-corrosive-metal-cracker-cells for precise stoichiometric control over materials such as antimony and tellurium
- In-situ RHEED to monitor epitaxial growth
- Substrate temperature range -100° to 1200°C
Organics Molecular Beam Epitaxy
This system has been purpose built for the deposition of a wide range of molecular and organic materials such as fullerenes, metallo-fullerenes, pthalocyanines and quinolines. Combined with an e-beam evaporator, this enables the growth of hybrid metal-organic devices with multiple organic components.
- Four low temperature effusion cells for precisely controlled evaporation of organic molecules
- Four pocket e-beam evaporation system for growth of metals
- DC/RF magnetron sputtering gun for growth of metals and metal-oxides
- Substrate temperature range from -100° to 1200°C
Pulsed Laser Deposition
This chamber is designed for the growth of complex oxides, including dielectrics such as STO, ferroelectrics and multi-ferroics.
- Multi-target system for growth of complex multi-layers
- KrF, 248 nm pulsed laser
- In-situ RHEED to monitor epitaxial growth
- Sample temperature range from room temperature to 1000°C
Sputtering
This system is dedicated to the development of complex multi-layer structures for research into fundamental magnetism and skyrmions, and growth of magnetic oxides such as YIG for development of spin-pumping devices.
- Eight DC/RF-magnetron sputter sources providing a wide range of magnetic and non-magnetic metals
- Off-axis sputter source for low-energy deposition onto sensitive materials
- Sample temperature range from -100° to 1200°C
Additional Resources
Application notes
Case studies
Research highlights